Vim基础篇(三十)——Debug插件vimspector
Vim基础篇(三十)——Debug插件vimspector
前言:
在linux下编程,终端最是常用的工具,将Vim和Terminal配合好使用将大大提高效率。
1 介绍
vimspector 是一个为Vim和Neovim提供图形化调试功能的插件,它使得在Vim中进行代码调试变得更加直观和高效。vimspector支持多种编程语言(如Python、C/C++、JavaScript、Go、Java等),通过集成 Debug Adapter Protocol (DAP) 实现与各种调试器的通信。
- 多语言支持 : 借助 DAP 协议,vimspector 可以支持任何实现了对应 Debug Adapter 的语言,例如:
- Python(使用
debugpy) - C/C++/Rust(使用
lldb-vscode或gdb) - JavaScript/TypeScript(使用
vscode-node-debug2) - Go(使用
delve) - Java、Ruby、PHP 等也都有相应支持
- Python(使用
- 可视化调试界面 : 在 Vim 中通过分割窗口显示:
- 断点列表
- 调用堆栈(Call Stack)
- 变量和作用域(Variables/Scopes)
- 表达式求值(Evaluate expressions)
- 控制按钮(继续、单步进入、跳出等)
- 配置灵活 : 使用 .vimspector.json 文件或全局配置来定义不同项目的调试设置,支持多个调试配置并可选择启动。
- 基于标准协议 : 使用微软提出的 **Debug Adapter Protocol (DAP)**,兼容 Visual Studio Code 的许多调试适配器。
- 操作便捷 : 支持快捷键设置断点、单步执行、查看变量值等,无需离开 Vim 编辑环境。
2 安装
以vim-plug插件举例安装,在 .vimrc 文件中添加以下配置。
1 | Plug 'puremourning/vimspector' |
在vim中执行指令安装c/c++调试器,安装命令如下。
1 | :VimspectorInstall vscode-cpptools |
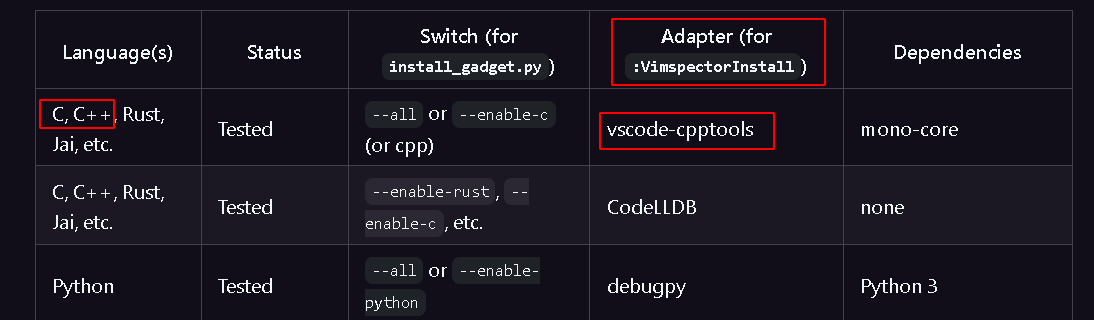
也可将python3的支持安装上。
1 | :VimspectorInstall debugpy |
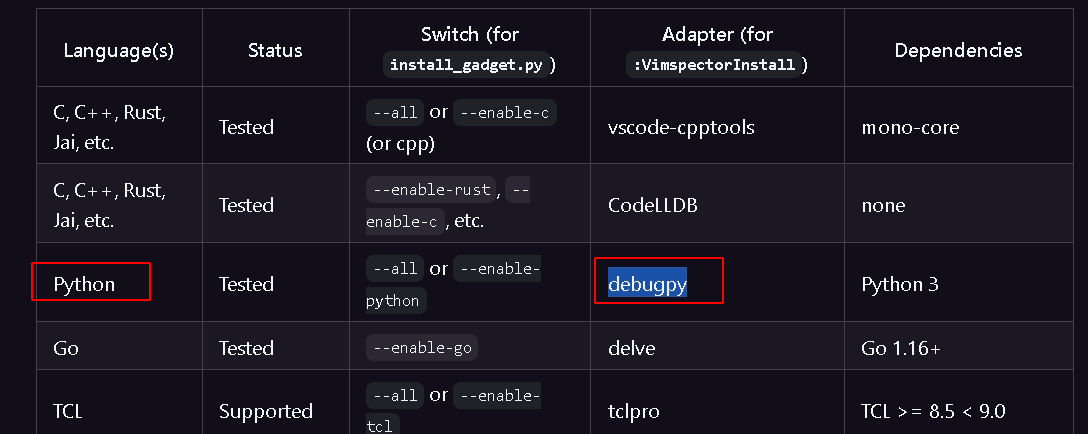
等待安装成功提示。
3 配置
在 .vimrc 中进行如下配置,主要是配置按键映射。使用作者默认的案件映射则配置如下。
1 | let g:vimspector_enable_mappings = 'HUMAN' |
| 按键 (Key) | 映射键 (Mapping) | 功能 (Function) |
|---|---|---|
F5 |
<Plug>VimspectorContinue |
调试时继续执行,否则开始调试。 |
F3 |
<Plug>VimspectorStop |
停止调试。 |
F4 |
<Plug>VimspectorRestart |
使用相同的配置重启调试。 |
F6 |
<Plug>VimspectorPause |
暂停被调试的程序。 |
F9 |
<Plug>VimspectorToggleBreakpoint |
在当前行切换(设置/取消)行断点。 |
<leader>F9 |
<Plug>VimspectorToggleConditionalBreakpoint |
在当前行切换条件断点或日志点。 |
F8 |
<Plug>VimspectorAddFunctionBreakpoint |
为光标下的表达式添加函数断点。 |
<leader>F8 |
<Plug>VimspectorRunToCursor |
运行到光标所在行。 |
F10 |
<Plug>VimspectorStepOver |
单步跳过(不进入函数)。 |
F11 |
<Plug>VimspectorStepInto |
单步进入(进入函数)。 |
F12 |
<Plug>VimspectorStepOut |
单步跳出(执行完当前函数)。 |
使用vscode风格的案件映射则配置如下。这个配置组合键太多,实际操作太麻烦,所以作者推荐 HUMAN 配置。
1 | let g:vimspector_enable_mappings = 'VISUAL_STUDIO' |
| 按键 (Key) | 映射键 (Mapping) | 功能 (Function) |
|---|---|---|
F5 |
<Plug>VimspectorContinue |
调试时继续执行,否则开始调试。 |
Shift F5 |
<Plug>VimspectorStop |
停止调试。 |
Ctrl Shift F5 |
<Plug>VimspectorRestart |
使用相同的配置重启调试。 |
F6 |
<Plug>VimspectorPause |
暂停被调试的程序。 |
F8 |
<Plug>VimspectorJumpToNextBreakpoint |
跳转到当前文件中的下一个断点。 |
Shift F8 |
<Plug>VimspectorJumpToPreviousBreakpoint |
跳转到当前文件中的上一个断点。 |
F9 |
<Plug>VimspectorToggleBreakpoint |
在当前行切换(设置/取消)行断点。 |
Shift F9 |
<Plug>VimspectorAddFunctionBreakpoint |
为光标下的表达式添加函数断点。 |
F10 |
<Plug>VimspectorStepOver |
单步跳过(不进入函数)。 |
Ctrl F10 |
<Plug>VimspectorRunToCursor |
运行到光标所在行。 |
F11 |
<Plug>VimspectorStepInto |
单步进入(进入函数)。 |
Shift F11 |
<Plug>VimspectorStepOut |
单步跳出(执行完当前函数)。 |
Alt 8 |
<Plug>VimspectorDisassemble |
显示反汇编代码。 |
也可以根据自己喜好修改映射,比如我的配置如下。
1 | " puremourning/vimspector |
vimspector会在sign-column显示断点符号,与其他插件同时在一行显示时,会被优先级更高的覆盖,通常我们希望断点的优先级比其他插件更高,可以进行如下配置,数字越大优先级越高。
1 | let g:vimspector_sign_priority = { |
4 使用
4.1 配置vimspector
进行Debug,工程编译需要配置 -g 参数,它是GCC/G++编译器中用于生成调试信息(Debugging Information)的关键参数。它的主要作用如下。
- 生成符号表 : 在可执行文件中嵌入变量名、函数名、类型结构等符号信息。
- 关联源码 : 建立机器指令与源代码行号的映射关系。
- 保留代码结构 : 保留函数调用关系、局部变量作用域等高级语言信息。
比如cmake如下编写,指定编译类型为 Debug 。
1 | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.22) |
也可明确配置参数。
1 | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.22) |
在工程根目录配置文件 .vimspector.json ,以便vimspector知道怎么去调用调试器。以下分享我用来Debug STM32F103xE的配置,可直接在RAM调试(要调试的固件已经烧录过了,不需要重新烧录,直接调试则选 attach to OpenOCD )或固件有更新,先烧录后调试 (选 program then attach )。
1 | { |
.vimspector.json 文件里也可以写gdb指令,比如以下是用gdb指令实现的 program then attach 烧录加调试功能。
1 | "STM32 (flash then attach)": { |
4.2 Debug模式
在vim中执行指令调用API :call vimspector#Launch() ,或者根据按键映射按下快捷键进入Debug模式。
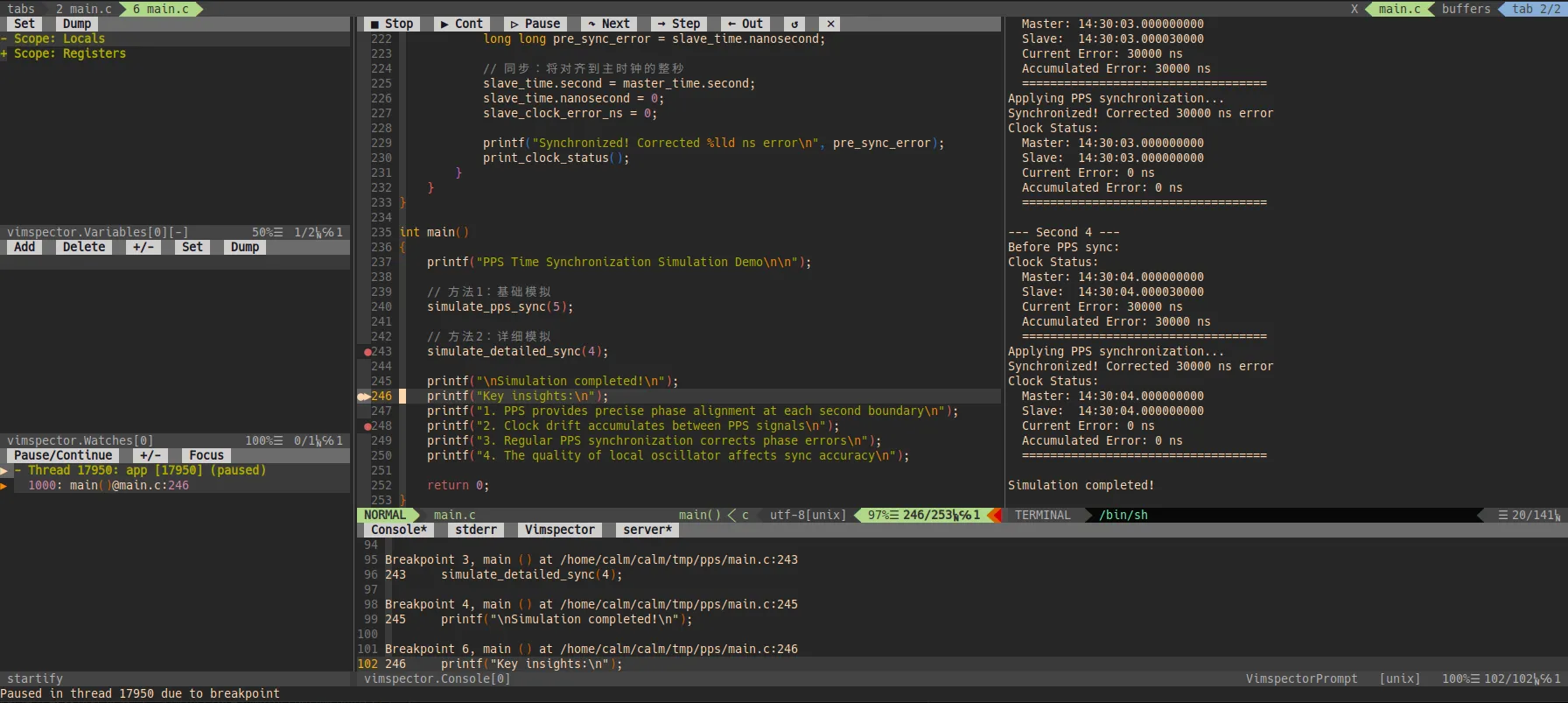
更多的API接口和案件映射接口如下。使用这些接口可以方便的控制程序的运行,打上断点。
| 映射键 (Mapping) | 功能 (Function) | 对应API调用 |
|---|---|---|
<Plug>VimspectorContinue |
调试时继续执行,否则开始调试 | vimspector#Continue() |
<Plug>VimspectorStop |
停止调试 | vimspector#Stop() |
<Plug>VimspectorRestart |
使用相同配置重新启动调试 | vimspector#Restart() |
<Plug>VimspectorPause |
暂停被调试的程序 | vimspector#Pause() |
<Plug>VimspectorBreakpoints |
显示/隐藏断点窗口 | vimspector#ListBreakpoints() |
<Plug>VimspectorToggleBreakpoint |
在当前行切换(设置/取消)断点 | vimspector#ToggleBreakpoint() |
<Plug>VimspectorToggleConditionalBreakpoint |
在当前行切换条件断点或日志点 | vimspector#ToggleBreakpoint({ trigger expr, hit count expr }) |
<Plug>VimspectorAddFunctionBreakpoint |
为光标下的表达式添加函数断点 | vimspector#AddFunctionBreakpoint('<cexpr>') |
<Plug>VimspectorGoToCurrentLine |
将当前程序计数器重置到当前行 | vimspector#GoToCurrentLine() |
<Plug>VimspectorRunToCursor |
运行到光标处 | vimspector#RunToCursor() |
<Plug>VimspectorStepOver |
单步跳过(不进入函数) | vimspector#StepOver() |
<Plug>VimspectorStepInto |
单步进入(进入函数) | vimspector#StepInto() |
<Plug>VimspectorStepOut |
单步跳出(执行完当前函数) | vimspector#StepOut() |
<Plug>VimspectorDisassemble |
显示反汇编。启用指令级单步 | vimspector#ShowDisassembly() |
<Plug>VimspectorUpFrame |
在当前调用栈中向上移动一帧(跳转到上一个栈帧) | vimspector#UpFrame() |
<Plug>VimspectorDownFrame |
在当前调用栈中向下移动一帧(跳转到下一个栈帧) | vimspector#DownFrame() |
<Plug>VimspectorJumpToNextBreakpoint |
将光标移动到当前文件中的下一个断点处 | vimspector#JumpToNextBreakpoint() |
<Plug>VimspectorJumpToPreviousBreakpoint |
将光标移动到当前文件中的上一个断点处 | vimspector#JumpToPreviousBreakpoint() |
<Plug>VimspectorJumpToProgramCounter |
将光标移动到当前帧的程序计数器所在位置 | vimspector#JumpToProgramCounter() |
<Plug>VimspectorBalloonEval |
在弹出窗口中评估光标下(或选中)的表达式 | internal |
也可用鼠标点击Vim界面上的虚拟按键。
4.3 Scope
显示当前作用域的变量值,可以按回车展开 + ,鼠标悬停也可查看变量值。
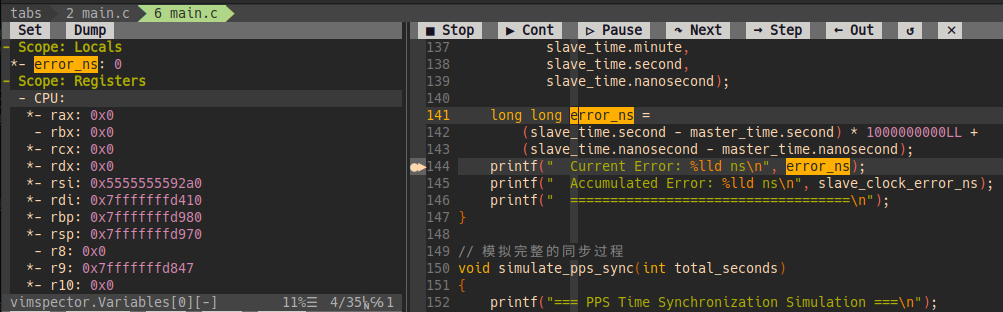
4.4 Watch
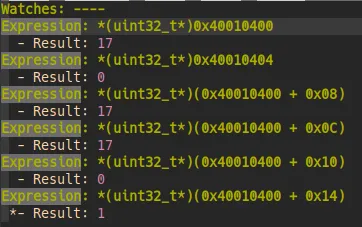
执行指令 :VimspectorWatch <expression> 可将表达式添加到 Watchs 窗口并显示其值。
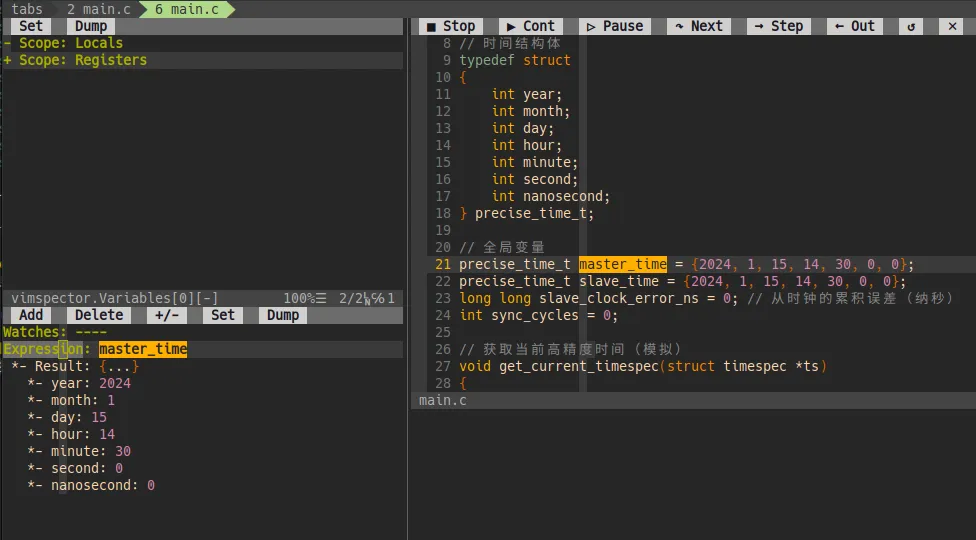
跟IDE一样,可以根据地址查看内存值。
4.5 GDB指令
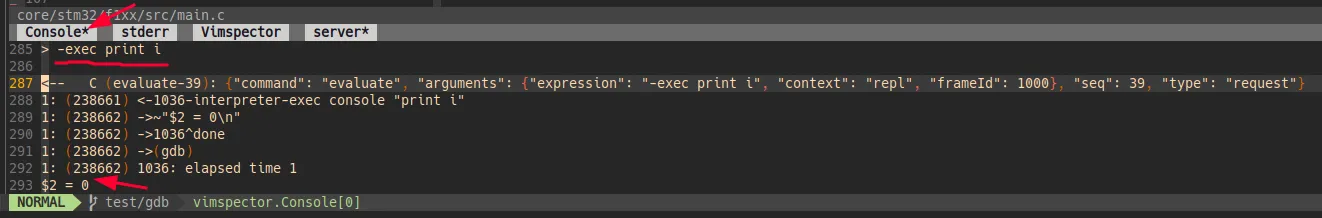
如果习惯使用原生的GDB指令进行调试,可以在vimspector控制台里直接执行GDB指令,以 vscode-cpptools 为例说明。
在vimspector界面的底部可以看到vimspector的控制台,光标在这里输入 i 即可进入插入模式输入指令,而GDB指令的语法格式为:
1 | -exec <GDB command> |
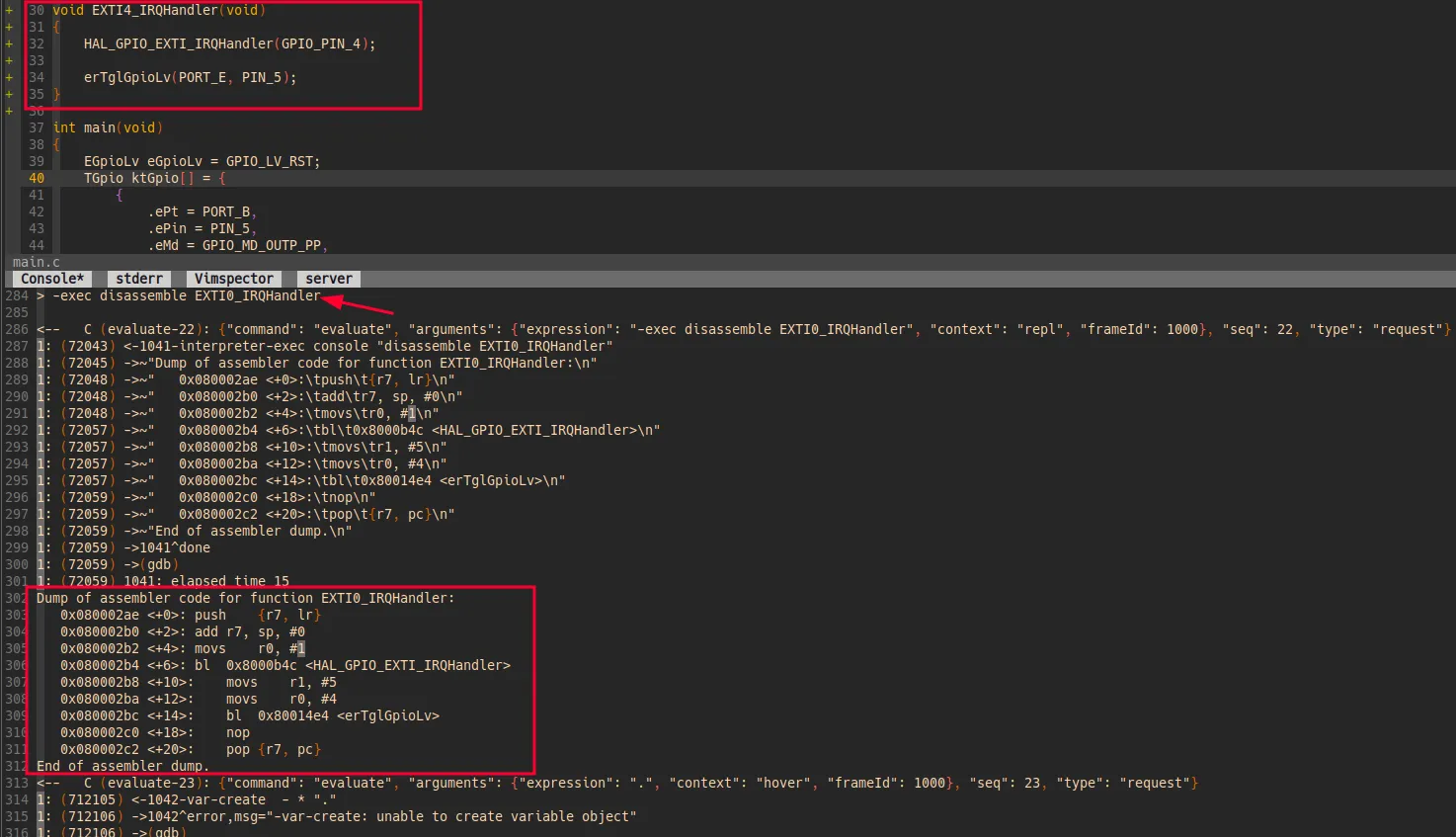
比如我查看变量 i 的值,其他GDB指令也都可以正常执行。
4.6 反汇编
执行指令 :VimspectorDisassemble 可打开反汇编窗口,为什么要查看反汇编代码?看到的c文件代码并不一定等于编译后实际执行的代码,比如有些工程滥用条件宏,而这些宏的定义可能藏在工程配置文件或编译构建脚本cmake或makefile中,导致一些IDE显示的有效代码块并不准确;另一种情况是工程内糟糕的定义了多个同名函数,之所以编译没有报错是通过构建工具cmake等进行了范围隔离,在一些超大型项目中,c的命名规则要完全避免重名是有难度的;又或者是虚函数的重定义,多个定义通过宏来屏蔽。最常见的是修改代码后没有生效,一些工程的构建规则并不健壮,变更没有被真正编译进去但却提示编译成功。这些情况的最有效的排查方法查看反汇编代码,才能知道实际生效的代码“真相”。总之,嵌入式开发需要会查看反汇编代码,帮助我们排查问题。
打开反汇编窗口后,光标在c文件中的跳转,反汇编窗口里的光标也会对应同步跳转,方便对应查看。
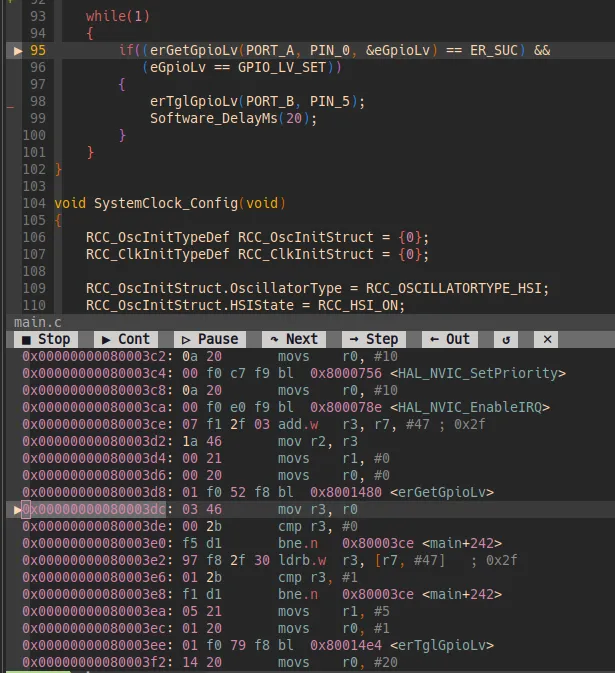
有时候我们想查看指定函数的反汇编代码,也可借助GDB指令查看指定函数的反汇编代码。